-
Research article
-
Assessment of composting potential of screened and decanter-separated pig slurry solids based on oxygen uptake rate
산소소모율을 이용한 돈슬러리 고액분리 고형물의 퇴비화 잠재성 평가
-
Yongwoo Song, Abera Jabessa Fufa, Heekwon Ahn
송용우, FufaAbera Jabessa, 안희권
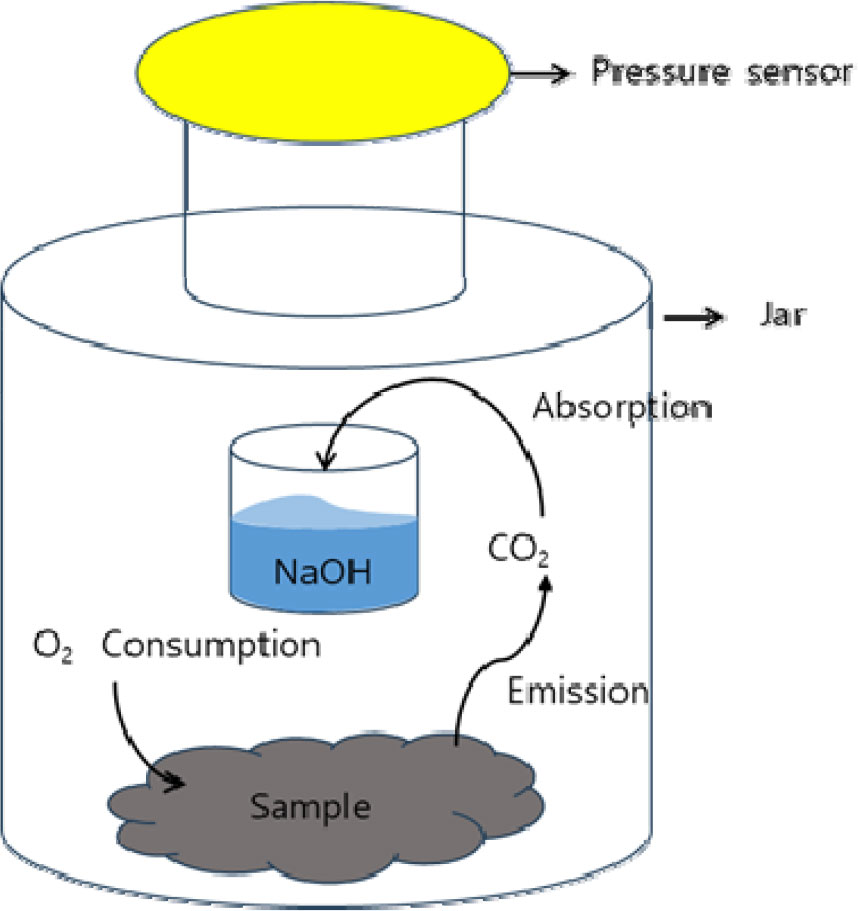
- This study was conducted to identify appropriate composting conditions for solids separated during the pretreatment processes of pig slurry treatment system, specifically …
- This study was conducted to identify appropriate composting conditions for solids separated during the pretreatment processes of pig slurry treatment system, specifically focusing on primary solid-liquid separation using a screen and secondary solid-liquid separation using a decanter, through the evaluation of oxygen uptake rate (OUR). Seven treatment groups were used to compare primary screened solids (T1), secondary decanter-separated solids (T2), mixtures of primary and secondary solids without bulking agents (T3 and T5), and additional treatments incorporating sawdust as a bulking agent with different mixing ratios (T4, T6, and T7). OUR was evaluated to assess the biodegradability of different solid fractions. Oxygen uptake rates ranged from 7.1 to 14.2 mg O2/g VS·d. The highest value observed in T2 (secondary decanter-separated solids). Lower oxygen uptake rates were observed in sawdust-amended treatments, indicating reduced microbial activity. This suggests that secondary decanter-separated solids contain more readily biodegradable organic matter and provide a favorable environment for composting. The reduced oxygen uptake rate in sawdust-amended treatments was likely attributable to excessive C/N ratios and the presence of lignin-rich recalcitrant material. Additionally, the increased porosity in sawdust mixtures may have contributed to a substrate dilution effect. Treatments combining both screened and secondary decanter-separated without bulking agents (T3) and (T5) exhibited intermediate OUR 10.3 and 11.5 mg O2/g VS·d, respectively. Overall, these findings demonstrate that secondary decanter-separated solids (T2) represents the most suitable fraction for composting, whereas sawdust addition requires careful optimization to avoid nitrogen limitation. - COLLAPSE
-
Assessment of composting potential of screened and decanter-separated pig slurry solids based on oxygen uptake rate
-
Research article
-
Study on odor-reduce effect of utilizing the Alcaligenes faecalis and Paracoccus denitrificans on solid excreta composting
가축분뇨의 퇴비화 처리 시 악취 저감을 위한 Alcaligenes faecalis 와 Paracoccus denitrificans의 활용에 관한 연구
-
Ju-Ho Park, Do-Hyeon Lee, Sin-Young Park
박주호, 이도현, 박신영
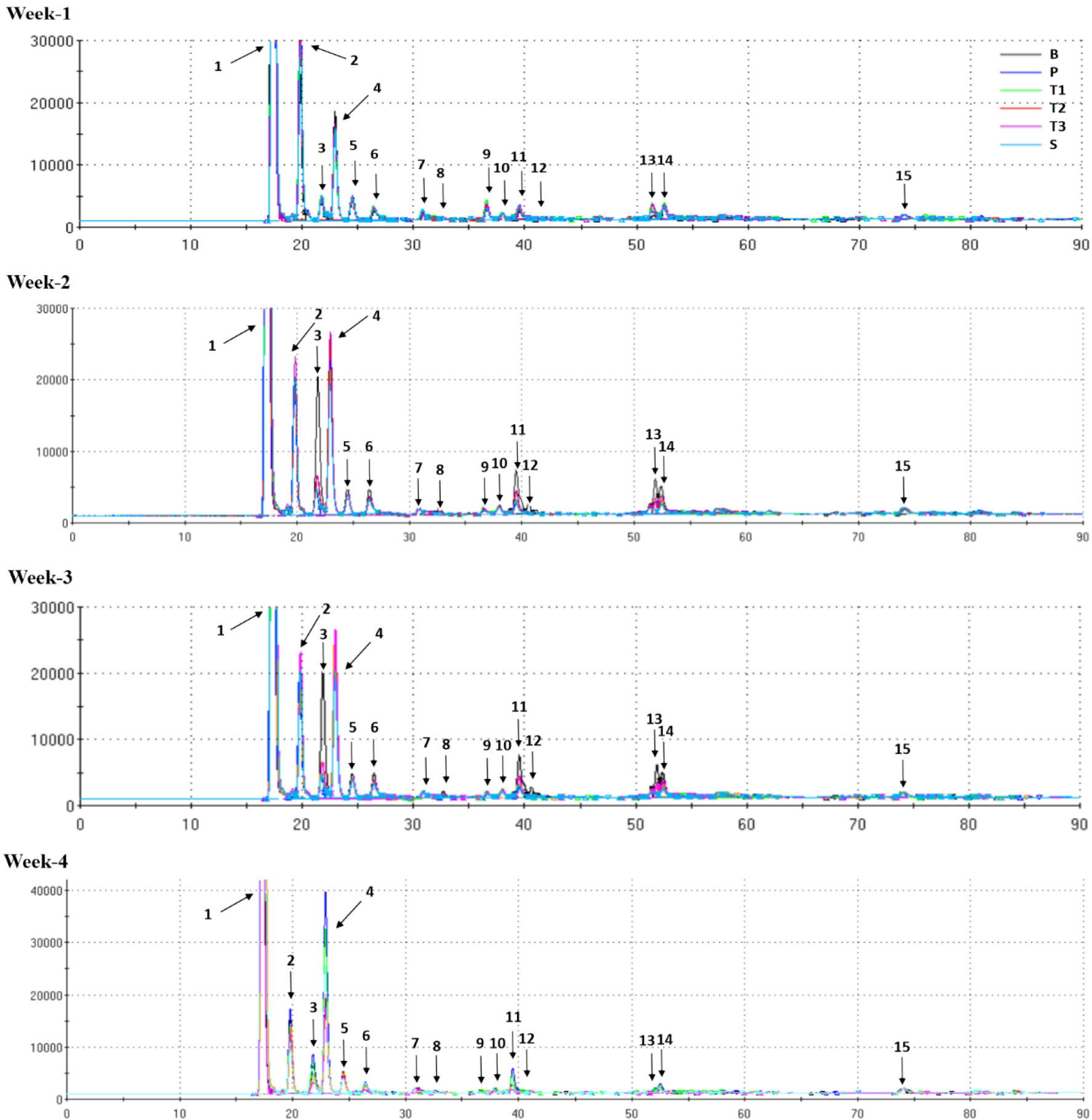
- This study investigated the effect of microbial additives on odor reduction during the composting of pig solid manure, utilized with Alcaligenes faecalis …
- This study investigated the effect of microbial additives on odor reduction during the composting of pig solid manure, utilized with Alcaligenes faecalis (KACC 19159, AF) and Paracoccus denitrificans (KACC 12251, PD). Composting treatments were performed using different mixing ratios of AF and PD (T1: 7:3, T2: 5:5, T3: 3:7), while Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S), Photosynthetic bacteria (P), and Bacillus subtilis (B) were used as controls. The composting process was conducted under anaerobic conditions for 4 weeks. Odor reduction efficiency and compost quality were evaluated through pH, CIE color, moisture content, electronic nose, and sensory evaluation. The pH of the samples changed under the four typical phases of composting, indicating stable decomposition. The T3 sample exhibited a desirable color with lower redness compared to the other samples. The moisture content showed no significant differences among treatments. Volatile compounds such as dimethyl sulfide and toluene were effectively reduced in the T3 sample, as confirmed by electronic nose analysis. Sensory evaluation also demonstrated that the T3 sample received the highest scores in odor and overall appearance. In conclusion, the combined use of AF and PD, particularly at a 3:7 ratio, proved effective in reducing odors and improving compost quality during anaerobic composting of pig manure. - COLLAPSE
-
Study on odor-reduce effect of utilizing the Alcaligenes faecalis and Paracoccus denitrificans on solid excreta composting
-
Research article
-
Effects of odor management practices on MSY and odor emission in domestic swine farms
국내 양돈농가의 악취요인 관리가 모돈두당연간출하두수 및 악취발생에 미치는 영향
-
Sang-Cheol Lee, Hyun-Sik Cheon, Jae-Hyeong Shin
이상철, 천현식, 신재형
- This study examined how the management of major odor-related factors in swine farms affects farm productivity, measured as marketed pigs per sow …
- This study examined how the management of major odor-related factors in swine farms affects farm productivity, measured as marketed pigs per sow per year (MSY). A total of forty commercial farms across Korea were surveyed using a ten-item odor management index that covered four main areas, namely feeding management, housing and ventilation, cleanliness, and pit management. Correlation and multiple regression analyses were carried out to determine how each management factor was related to official MSY records. The overall odor management score showed a strong positive association with MSY (r=0.73, p<0.001). Among the individual indicators, barn ventilation, growth-stage feeding system, and slurry pit cleaning were found to have independent and significant effects on MSY (β=0.214, 0.187, and 0.176; all p≤0.01). To further explore these relationships, a field trial was conducted to assess how slurry storage duration influences ammonia concentration. Farms that removed slurry every three weeks maintained around 17% lower average ammonia levels than farms without removal, and the difference became more evident during the late fattening phase (days 44~60, p<0.05). Overall, the findings suggest that effective management of odor-related factors can directly enhance productivity in swine farms. Improving ventilation, applying precise feeding by growth stage, and maintaining regular pit cleaning can serve as practical and achievable measures for producers. These results provide valuable field-based evidence that may help guide future odor management practices and policy planning aimed at sustainable productivity improvement in the pig industry. - COLLAPSE
-
Effects of odor management practices on MSY and odor emission in domestic swine farms
-
Short communication

-
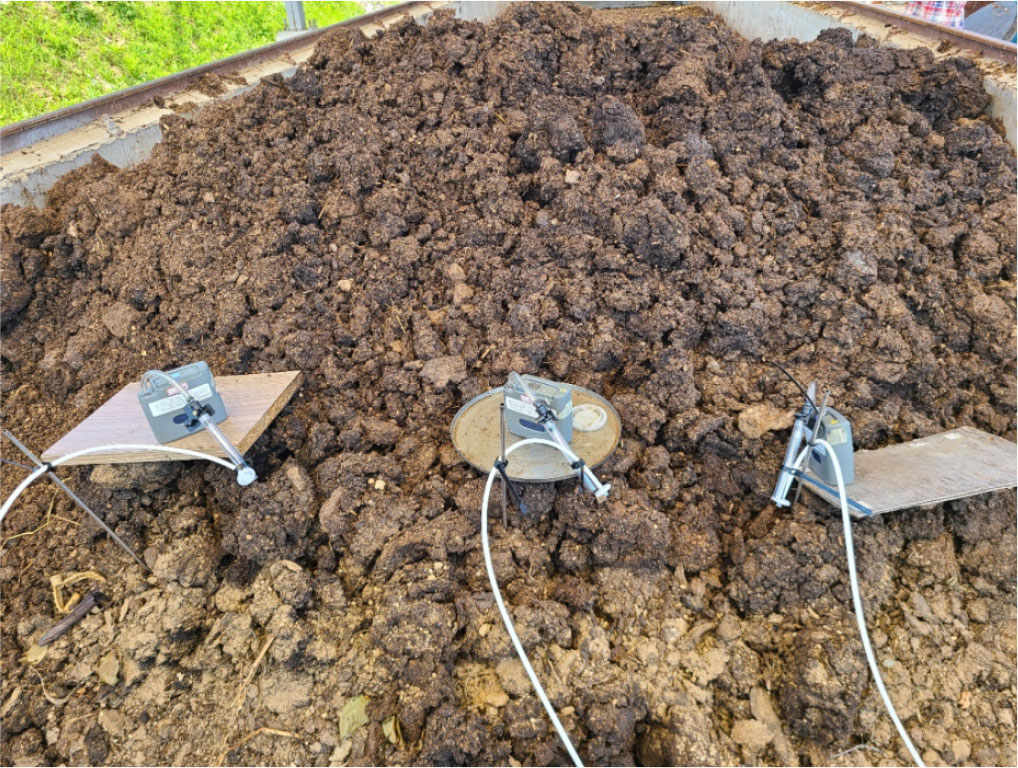
Sensor reliability verification for measurement of ammonia generation by composting livestock manure
가축분뇨 퇴비화에 따른 암모니아 발생량 측정을 위한 센서 신뢰도 검증
-
Woo Je Lee, Ki Youn Kim
이우제, 김기연
- Livestock accounted for six of the top ten agricultural products in South Korea, reflecting its significant role in the sector. However, industrialization …
- Livestock accounted for six of the top ten agricultural products in South Korea, reflecting its significant role in the sector. However, industrialization and specialization in livestock farming have increased livestock manure production and odor complaints. Key odorants include ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and methyl mercaptan, with ammonia being the most prevalent. Ammonia not only causes odor but also contributes to PM2.5 formation, impacting environmental quality. This study aimed to measure ammonia emission factors during livestock manure composting using a flux chamber. Current Korean air pollution testing standards specify methods such as non-dispersive infrared spectroscopy and solution conductivity for ammonia measurement, but real-time, quasi-continuous monitoring alongside other greenhouse gases requires specialized sensors. A laser-based ammonia sensor, measuring every 67.5 seconds with a 0-100 ppm range, was tested for reliability against the NIOSH Method 6015. Measurements were conducted in a cattle manure aerated static pile facility at three locations using both the laser sensor and solid sorbent tubes. Sampling took place in June 2023 over 2.5 hours. Average sensor readings were 1,236.1, 962.2, and 1,142.7 ppb, while sorbent tube results were 1,227.4, 975.7, and 1,162.1 ppb, respectively. The overall average error was within 1%. The results confirm that the laser sensor provides ammonia measurements comparable to the standard method, supporting its potential for real-time monitoring of emissions from manure composting. - COLLAPSE
-
Sensor reliability verification for measurement of ammonia generation by composting livestock manure
-
Research article
-
Evaluation of the effectiveness of floating cover combined with aerobically treated pig slurry recharge for reducing hydrogen sulfide emissions in swine barns
액비 투입과 연계한 Floating Cover 적용에 따른 돈사 황화수소 배출량 저감 효과 평가
-
Seongjun Park, Seunghun Lee, Jinho Shin, Riuh Wardhani, Abera Jabessa Fufa, Yongwoo Song, Dongyeo Kim, Ilhwan Song, Heekwon Ahn
박성준, 이승훈, 신진호, RiuhWardhani, Abera JabessaFufa, 송용우, 김동여, 송일환, 안희권
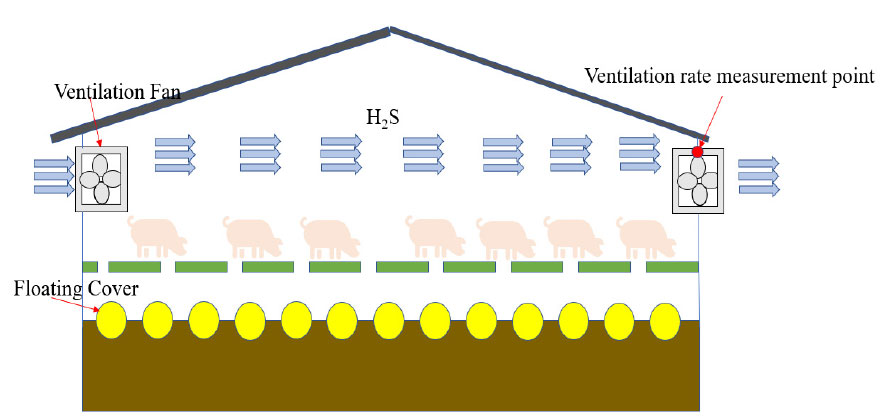
- This study investigated the effectiveness of a floating cover made of multiple floating balls in reducing hydrogen sulfide (H2S) emissions …
- This study investigated the effectiveness of a floating cover made of multiple floating balls in reducing hydrogen sulfide (H2S) emissions from a swine nursery slurry pit, which was pre-filled with aerobically treated slurry to 30% volume. H2S emissions were monitored across two phases: a non-rearing period and an 8-week rearing period. Initially, the cover proved effective, achieving a 49% reduction in area-based H2S emissions compared to the control during the non-rearing phase. However, a temporary spike in H2S was observed in the treated group during the first week after pig placement. This increase was likely due to physical agitation of the slurry surface caused by the animals entering the barn. Despite this initial peak and subsequent manure accumulation, the floating cover consistently reduced emissions thereafter. The cover achieved a significant 62% reduction in H2S emissions (p < 0.05) over the entire rearing period, demonstrating sustained mitigation performance under operational conditions. Importantly, the substantial reduction in H2S volatilization did not translate into a measurable difference in nursery pig productivity; average daily gain (ADG) was similar between the treatment and control groups (p > 0.05). Overall, the floating cover offers a practical and effective strategy for mitigating H2S emissions in swine housing. Further field-based studies are recommended to confirm its long-term applicability and effectiveness at a commercial scale under varying operational conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of the effectiveness of floating cover combined with aerobically treated pig slurry recharge for reducing hydrogen sulfide emissions in swine barns
-
Research article
-
Evaluation of greenhouse gas emission potential of agricultural by-products: A comparison of rumen in vitro digestibility, IPCC tier 2 equations based on life cycle inventory databases
국내 농업 부산물의 온실가스 배출 잠재력 평가: 전 과정 목록 데이터베이스 기반 반추위 체외 소화율 및 IPCC 2단계 방정식 비교
-
Youngjun Na, Jun Sik Woo, Na Kyun Lee, Keun Kyu Park, Yoosung Park, Yongjun Choi
나영준, 우준식, 이나균, 박근규, 박유성, 최용준
- This study evaluated the methane emission potential of major feed ingredients and agricultural by‑products used in Korean ruminant systems by comparing three …
- This study evaluated the methane emission potential of major feed ingredients and agricultural by‑products used in Korean ruminant systems by comparing three approaches: rumen in vitro digestibility, the 2019 IPCC Tier 2 equations, and life cycle inventory (LCI) databases. Ten conventional feeds and ten agricultural by‑products were selected based on domestic use or generation volume and classified as fibrous, protein, or energy sources. Their chemical composition (proximate analysis, fiber fractions, gross energy) and rumen in vitro gas production, methane production, and digestibility were measured to derive enteric methane emission factors and corresponding CO2‑equivalent values. IPCC Tier 2‑based methane factors were estimated from feed energy and NDF levels, while LCI‑based emissions for feed production were obtained from Agri‑Footprint and Ecoinvent. Methane emission factors derived from in vitro digestibility were generally higher than those from IPCC equations, and the three methods often produced markedly different values for the same ingredient, indicating strong method dependence of emission estimates. Some by‑products, including lupin seed, beet pulp, and cabbage/Chinese cabbage by‑products, showed relatively low enteric methane emission factors per unit of digestible energy and lower production‑stage emissions, suggesting mitigation potential when they partially replace cereals or conventional forages. However, in vitro fermentation reflects substrate‑specific fermentation more sensitively than animal‑level intake and passage dynamics, IPCC Tier 2 relies on generalized Ym/MY coefficients not fully validated for by‑product‑rich Korean rations, and foreign LCI databases may misrepresent domestic production conditions. Therefore, this study was conducted to evaluate the greenhouse gas emission potential of domestic feed resources and agricultural by-products by comparing rumen in vitro digestibility, the IPCC Tier 2 method, and whole life cycle inventory databases. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of greenhouse gas emission potential of agricultural by-products: A comparison of rumen in vitro digestibility, IPCC tier 2 equations based on life cycle inventory databases
-
Research article

-
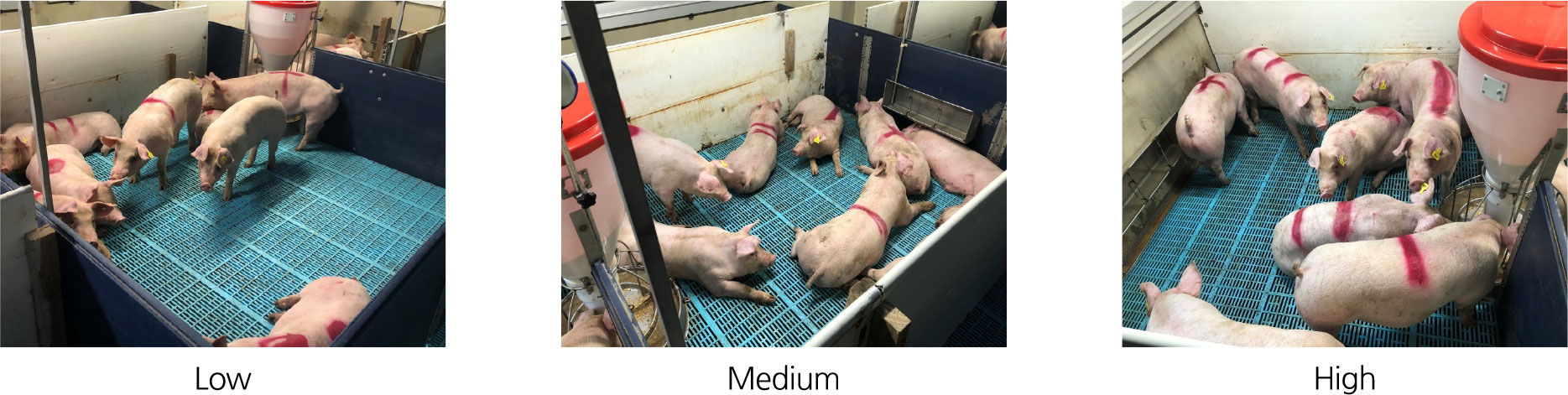
Effects of stocking density and toy provision on stress related abnormal behavior and productivity of finishing pigs
사육밀도와 장난감 제공이 비육돈의 스트레스 관련 이상행동 및 생산성에 미치는 영향
-
Tea-Hwan Park, Duck‐Min Ha, Doo‐Hwan Kim
박태환, 하덕민, 김두환
- This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of environmental improvement in pig farms on the behavior and productivity of finishing pigs. …
- This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of environmental improvement in pig farms on the behavior and productivity of finishing pigs. Specifically, the impacts of different space allowances per pig (1.0 m², 0.8 m², and 0.6 m²) and the provision of toy were compared in terms of stress related abnormal behaviors, growth performance, and carcass quality. The frequency of abnormal behaviors increased as stocking density became higher, whereas pigs reared under low density conditions exhibited significantly greater average daily gain, carcass weight, backfat thickness, and higher carcass grading scores (P<0.01). The provision of toy significantly reduced the occurrence of aggressive behaviors and improved weight gain (P<0.01). Moreover, pigs without toy showed a higher frequency and longer duration of bothering behaviors. In conclusion, maintaining a space allowance of at least 0.8 m² per finishing pig and providing environmental enrichment materials can effectively reduce stress and enhance productivity. These findings suggest that optimal stocking density and environmental enrichment may serve as a basis for transitioning conventional pig farms toward welfare enriched production systems that ensure both animal welfare and economic sustainability. - COLLAPSE
-
Effects of stocking density and toy provision on stress related abnormal behavior and productivity of finishing pigs
-
Research article

-
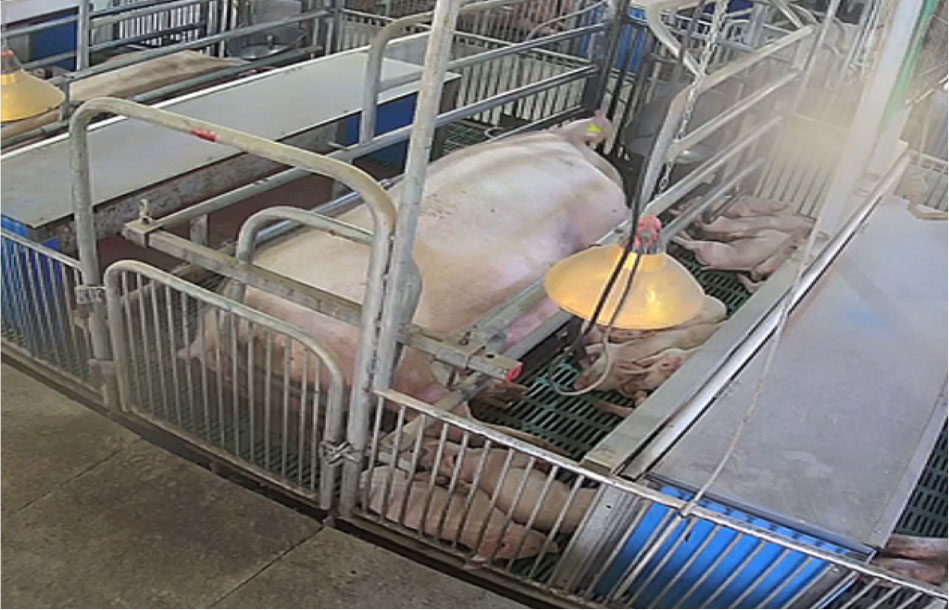
Effects of welfare enriched farrowing facility on behavior and productivity of farrowing sows and suckling piglets
복지형 분만시설이 모돈과 자돈의 행동 및 생산성에 미치는 영향
-
Tea-Hwan Park, Duck‐Min Ha, Doo‐Hwan Kim
박태환, 하덕민, 김두환
- This study investigated the effects of improving animal welfare in pig farms on the behavior and productivity of farrowing sows and piglets. …
- This study investigated the effects of improving animal welfare in pig farms on the behavior and productivity of farrowing sows and piglets. The behavioral characteristics and production performance of farrowing sows and suckling piglets housed in either conventional farrowing crates or welfare enriched farrowing pens were compared and analyzed. In both types of farrowing facilities, lateral lying was the most frequently observed behavior among sows, followed by ventral lying. The frequency of ventral lying was significantly higher in sows housed in farrowing crates than in those in welfare enriched pens (P<0.05). Sitting occurred least frequently in both facilities, with no significant difference between treatments. Standing showed a similar trend, whereas eating occurred more than twice as often as either sitting or standing. Among piglets, lying accounted for the majority of their observed behaviors, with no significant difference between the two farrowing environments. However, walking was observed more frequently in piglets housed in welfare enriched pens (P<0.01), while suckling occurred more frequently among piglets in conventional crates (P<0.01). Sows in welfare enriched pens exhibited a significantly higher feed intake compared with those in farrowing crates (P<0.05). However, body weight change, weaning-to-estrus interval, and backfat thickness did not differ significantly between treatments. Similarly, piglet growth performance during the 24-day lactation period showed no significant differences between farrowing systems. In conclusion, the operation of welfare enriched farrowing facilities did not negatively affect the productivity of sows or piglets and is expected to enhance animal welfare without compromising production performance. - COLLAPSE
-
Effects of welfare enriched farrowing facility on behavior and productivity of farrowing sows and suckling piglets
-
Research article
-
Analysis of indoor temperature-humidity index in pig housing using building energy simulation
BES 기법을 활용한 돈사 내부 온습도 지수 분석
-
Han-Kyu Lee, Taehwan Ha
이한규, 하태환
- Recent global warming has increased the frequency of extreme weather events, intensifying heat stress in pigs and leading to a growing number …
- Recent global warming has increased the frequency of extreme weather events, intensifying heat stress in pigs and leading to a growing number of heat-related mortalities. This study aims to investigate the effects of various environmental and operational conditions on the thermal environment inside pig houses and to provide fundamental data for developing strategies to improve energy efficiency and climate resilience. A standard pig house model was developed based on the design guidelines of the Ministry of Agriculture using a Building Energy Simulation (BES) approach. A total of 256 simulations were conducted by combining region (16), weather dataset type (2), insulation level (4), and cooling system operation (2). Hourly indoor temperature and relative humidity were obtained from the simulations and used to calculate the Temperature-Humidity Index (THI). Four comparison groups were then established to evaluate variations in THI under different conditions. The results indicated that region, weather dataset type, and cooling system operation had significant effects on THI, whereas insulation level did not show a statistically significant influence. This study quantitatively demonstrates the relative impacts of regional, meteorological, insulation, and cooling conditions on the thermal environment of pig houses. The findings are expected to provide useful reference data for improving thermal environments in pig housing and for establishing strategies related to energy efficiency and climate adaptation. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of indoor temperature-humidity index in pig housing using building energy simulation
-
Research article

-
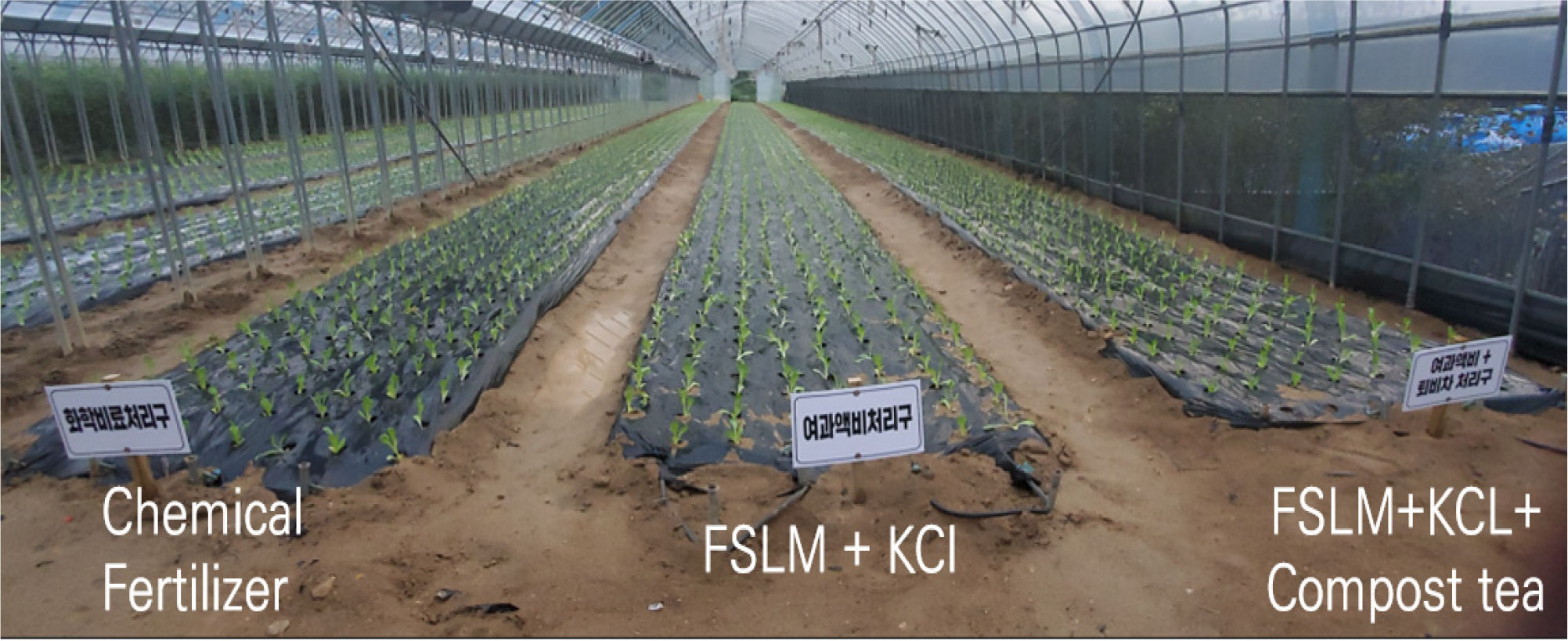
Effect of filtered swine liquid manure on the farmer’s income and yield of Lactuca sativa longifolia, Asteraceae
여과 액비 사용이 로메인 상추의 수량과 농가 소득에 미치는 영향
-
Deog-Bae Lee, Byoung-O Lee, Byeonghyeon Kang, Kiyong Nam, Hyun-Shik Choi
이덕배, 이병오, 강병현, 남기용, 최현식
- 20-day-old romaine lettuce seedlings were transplanted on September 13 and harvested on October 25, 2024. Fertilizer usage was calculated based on soil …
- 20-day-old romaine lettuce seedlings were transplanted on September 13 and harvested on October 25, 2024. Fertilizer usage was calculated based on soil testing using the chemical fertilizer(CF), filtered swine liquid manure(FSLM)+potassium chloride(KCl), and FSLM+KCl+compost tea. The nitrogen content of the edible part of romaine lettuce was the highest in CF at 4.2%, but there were no statistically significant differences in phosphorus, potassium, calcium, or magnesium contents among the treatments. The differences in soil nutrient content before and after the experiment revealed a decrease in pH, organic matter, phosphate, potassium, calcium, and magnesium content as well as electric conductivity. The use of FSLM reduced chemical fertilizer usage by 56.3 kg per 10a, resulting in a savings of KRW 94,800 in fertilizer costs. FSLM+KCl resulted in more leaves and thicker taproots than CF. Consequently, marketable yield per 10a increased by 16.9% in FSLM+KCl and by 13.0% in FSLM+KCl+compost tea compared to CF. Adding the fertilizer cost savings by using FSLM, the total economic benefit of FSLM was KRW 915,200 per 10a. - COLLAPSE
-
Effect of filtered swine liquid manure on the farmer’s income and yield of Lactuca sativa longifolia, Asteraceae
-
Research article
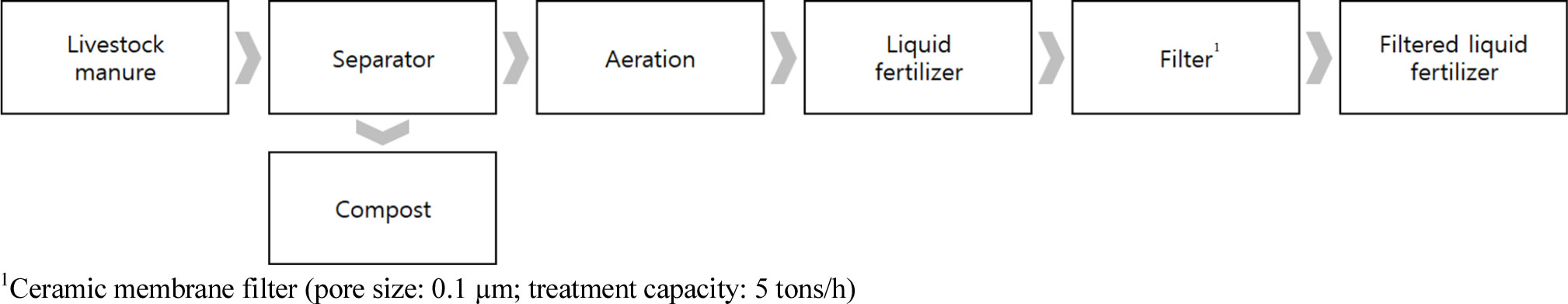
-
Evaluation of chemical fertilizer and farm cost savings through the use of filtered liquid fertilizer
여과액비 활용에 따른 화학비료 및 농가 경영비 절감 효과 평가
-
Soo-Ryang Kim, Ji-won Jung, Sung-Ha Hong, Byong-O Lee, Sun-Goo Hwang, Myung-Gyu Lee
김수량, 정지원, 홍성하, 이병오, 황선구, 이명규
- This case study evaluated the agronomic applicability and economic benefits of using filtered liquid fertilizer (FLF) derived from livestock manure for spinach …
- This case study evaluated the agronomic applicability and economic benefits of using filtered liquid fertilizer (FLF) derived from livestock manure for spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) greenhouse cultivation in Pocheon, Korea. The FLF was produced via a membrane filtration process and showed a reduced suspended solids content (SS, 684 mg/L), indicating suitability for fertigation systems. Chemical analysis revealed that the FLF contained high levels of total nitrogen (2,242.32 mg/L) and potassium (K2O, 2,640.62 mg/L), whereas phosphorus (P2O₅, 151.80 mg/L) was markedly lower than other major nutrients. Soil diagnosis of the study sites showed excessive accumulation of available phosphate (Av. P2O5, 1,028 mg/kg), far exceeding the recommended range, while nitrate-nitrogen was below the optimal range. Therefore, an FLF application strategy based on crop nitrogen requirements was considered optimal to supply nitrogen and potassium without aggravating phosphorus accumulation. Substituting chemical fertilizers with FLF resulted in a fertilizer cost saving of 47,193 KRW per 10a. Although the FLF exhibited high electrical conductivity (EC, 23.41 dS/m), the findings suggest that FLF can serve as an effective alternative to chemical fertilizers in intensive greenhouse systems, particularly for managing nutrient imbalance in phosphorus- accumulated soils while providing tangible economic benefits to farmers. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of chemical fertilizer and farm cost savings through the use of filtered liquid fertilizer
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Animal Environmental Science
Journal of Animal Environmental Science
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Animal Environmental Science
Journal of Animal Environmental Science








